What are the different types of photographic paper?
Paper can be divided into two main branches: Negative–positive and positive–positive. The characteristics discussed here are valid for both of these type of papers. With negative paper you need to use a negative to form an image, while positive paper prints can be generated without the need for a negative. Both are coated in an emulsion composed of silver halide crystals. When exposed to light, the crystals form a latent image that needs to be developed to be visible.
The second important distinction to make is between fixed grade and variable contrast paper. Fixed grade paper has a set contrast on a scale of 0–5, where 0 is soft contrast and 5 is hard. Variable contrast paper however allows for a broad range of contrast to be obtained from the negatives, which is achieved with the use of filters.


There are also different types of paper base. The two main base types are resin coated (RC) and fiber base (FB).
In RC paper, the emulsion is coated over the polyester and sealed between two layers of polyethylene that are resistant to water infiltration. This kind of paper is easier to handle and quicker to work with.
FB paper, also known as Baryta paper (barium sulphate is a chief ingredient in the emulsion) , is topped with a gelatin layer to protect the emulsion. FB papers are heavier in weight, have deeper blacks, and they are known to have a higher archival lifetime.
Due to their fiber nature, they are easier to retouch, as the ink will absorb into the paper easily. However they are more difficult to work with, because the porous nature of the paper requires more time to develop, stop, fix, and wash. Fixing and washing are especially delicate steps that should not be rushed.


Finally, there are a few kinds of finishing styles of paper: Matte, Pearl, Glossy, and Satin. The texture of the paper affects the tonal range of the final print and will determine the amount of deep blacks a photograph can reach.
Matte textured paper will reflect more light during the printing process, therefore the blacks will not reach a deep tone compared to glossy paper.
If choosing to work with glossy paper, the photographer should always wear gloves to avoid fingerprints and scratches. Be aware that the final print will reflect more light when hanging on a wall.
Pearl and satin are in between options. Pearl paper is closer to a glossy finish, and satin has a smooth finish without the shine of gloss or pearl but with all the contrast.
Anything missing?
Can’t find an answer to your question? Or do you have some useful advice to add to one of our courses? We want to build the world’s largest analogue learning space, so please send any further requests or information to school@lomography.com and we’ll take a look!
More Courses
-
How to make a darkroom at home?
When setting up a darkroom, it is crucial to find an adequate space and purchase a good enlarger. Every other tool can be easily found online.
-
What is a test strip?
A test strip is a piece of paper with which the correct exposure time for an image can be determined by dividing it into sections of different exposures.
-
What is a contact sheet?
A contact sheet is a printed photographic paper that includes on a single page all the photos taken on the roll.
-
What does “pre-flashing” mean?
Pre-flashing is done to the whole paper to accelerate the density, without compromising the white. It is used when there is a negative with dense highlights.
-
What is split grade printing?
Split grade printing refers to the use of more than one filter when printing your photos in a darkroom, in order to properly expose the highlights and shadow areas.
-
How and where to find a darkroom to use if you don’t have space at home?
In many cities you will be able to find darkrooms that you can use. These spaces are often part of a university, college or photography center.
-
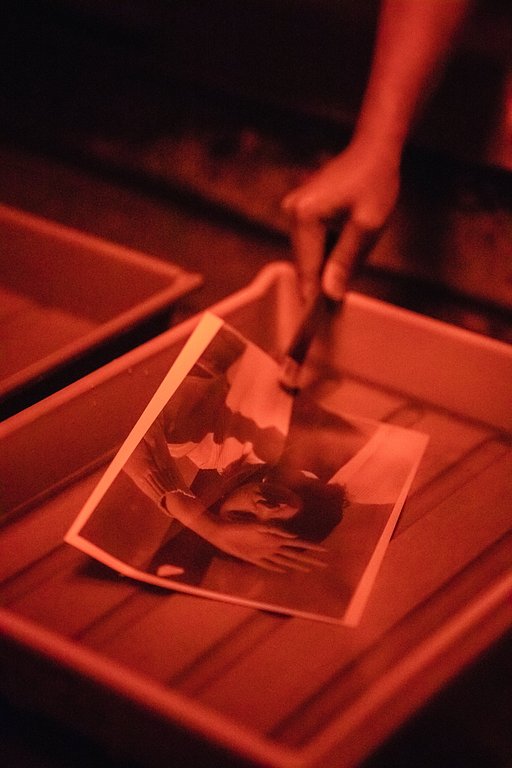
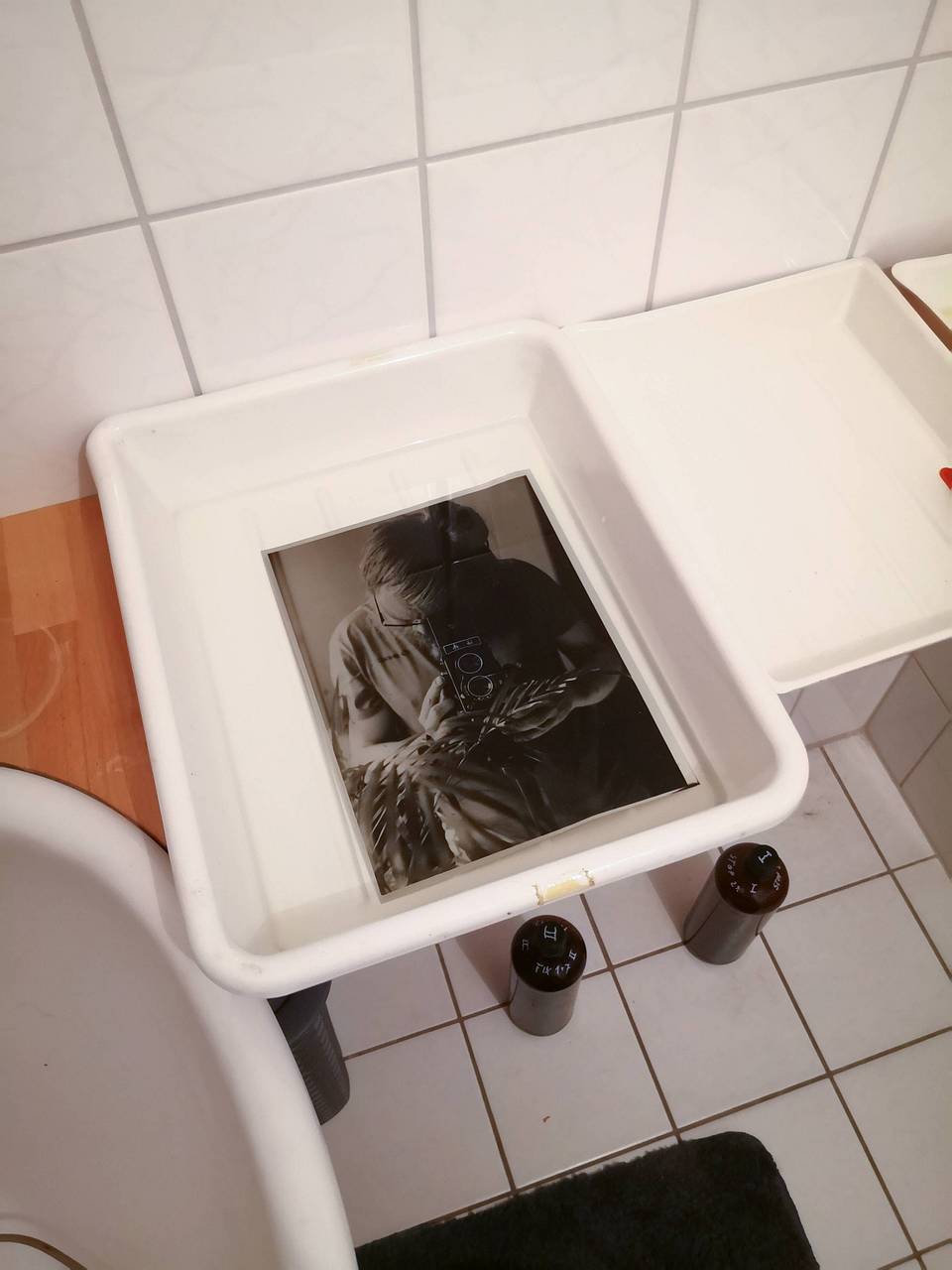
How to make a darkroom print
Work in a fully equipped darkroom. Select a negative, put it in an enlarger and focus the frame. Then expose the image for the correct time on the photographic paper. Finally develop, stop, fix, wash and dry.
-
What is an enlarger?
An enlarger is a light projector used to make a print of an image that is larger than the original negative or transparency.
-
What is Dodging and Burning?
Dodging and burning are darkroom techniques used to make adjustments to different areas of our prints. Dodging lightens an area, while burning darkens an area.